15. 异常
我们介绍Solidity三种抛出异常的方法:error,require和assert,并比较三种方法的gas消耗。
异常
写智能合约经常会出bug,Solidity中的异常命令帮助我们debug。
Error
error是solidity 0.8.4版本新加的内容,方便且高效(省gas)地向用户解释操作失败的原因,同时还可以在抛出异常的同时携带参数,帮助开发者更好地调试。人们可以在contract之外定义异常。下面,我们定义一个TransferNotOwner异常,当用户不是代币owner的时候尝试转账,会抛出错误:
error TransferNotOwner(); // 自定义error
我们也可以定义一个携带参数的异常,来提示尝试转账的账户地址
error TransferNotOwner(address sender); // 自定义的带参数的error
在执行当中,error必须搭配revert(回退)命令使用。
function transferOwner1(uint256 tokenId, address newOwner) public {
if(_owners[tokenId] != msg.sender){
revert TransferNotOwner();
// revert TransferNotOwner(msg.sender);
}
_owners[tokenId] = newOwner;
}
我们定义了一个transferOwner1()函数,它会检查代币的owner是不是发起人,如果不是,就会抛出TransferNotOwner异常;如果是的话,就会转账。
Require
require命令是solidity 0.8版本之前抛出异常的常用方法,目前很多主流合约仍然还在使用它。它很好用,唯一的缺点就是gas随着描述异常的字符串长度增加,比error命令要高。使用方法:require(检查条件,"异常的描述"),当检查条件不成立的时候,就会抛出异常。
我们用require命令重写一下上面的transferOwner1函数:
function transferOwner2(uint256 tokenId, address newOwner) public {
require(_owners[tokenId] == msg.sender, "Transfer Not Owner");
_owners[tokenId] = newOwner;
}
Assert
assert命令一般用于程序员写程序debug,因为它不能解释抛出异常的原因(比require少个字符串)。它的用法很简单,assert(检查条件),当检查条件不成立的时候,就会抛出异常。
我们用assert命令重写一下上面的transferOwner1函数:
function transferOwner3(uint256 tokenId, address newOwner) public {
assert(_owners[tokenId] == msg.sender);
_owners[tokenId] = newOwner;
}
在remix上验证
输入任意
uint256数字和非0地址,调用transferOwner1,也就是error方法,控制台抛出了异常并显示我们自定义的TransferNotOwner。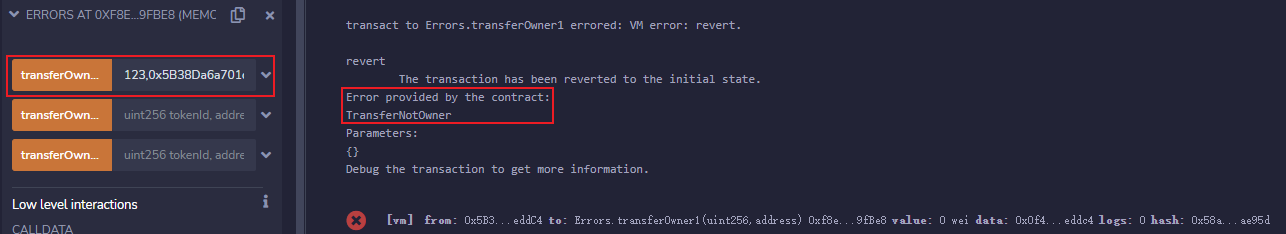
输入任意
uint256数字和非0地址,调用transferOwner2,也就是require方法,控制台抛出了异常并打印出require中的字符串。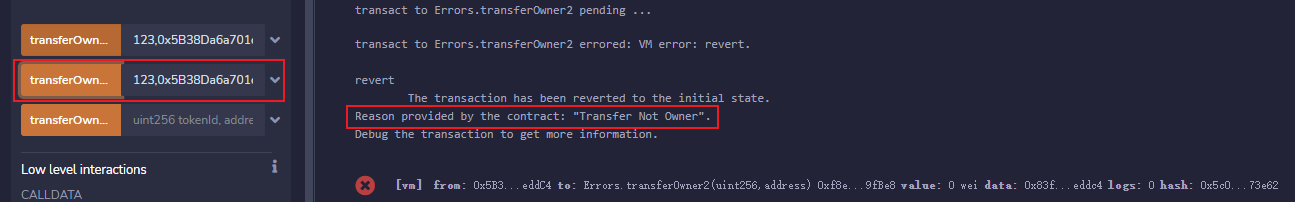
输入任意
uint256数字和非0地址,调用transferOwner3,也就是assert方法,控制台只抛出了异常。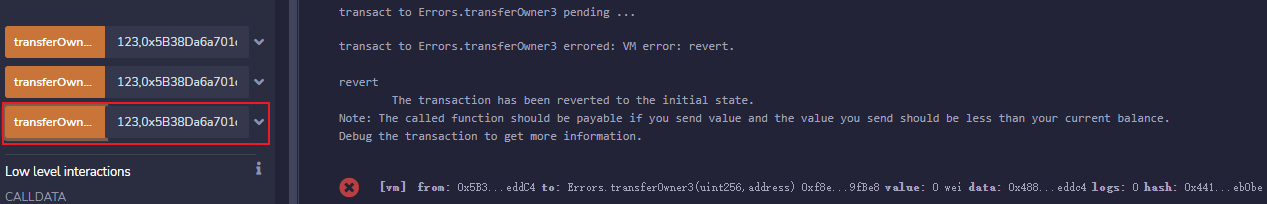
三种方法的gas比较
我们比较一下三种抛出异常的gas消耗,通过remix控制台的Debug按钮,能查到每次函数调用的gas消耗分别如下: (使用0.8.17版本编译)
error方法gas消耗:24457 (加入参数后gas消耗:24660)require方法gas消耗:24755assert方法gas消耗:24473
我们可以看到,error方法gas最少,其次是assert,require方法消耗gas最多!因此,error既可以告知用户抛出异常的原因,又能省gas,大家要多用!(注意,由于部署测试时间的不同,每个函数的gas消耗会有所不同,但是比较结果会是一致的。)
备注: Solidity 0.8.0之前的版本,assert抛出的是一个 panic exception,会把剩余的 gas 全部消耗,不会返还。更多细节见官方文档。
完整合约
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.21;
// Gas cost在Remix中测试得到 使用0.8.17版本编译
// 参数使用 tokenId = 123, address = {any address}
// 自定义error
error TransferNotOwner();
// error TransferNotOwner(address sender);
contract Errors {
// 一组映射,记录每个TokenId的Owner
mapping(uint256 => address) private _owners;
// Error方法: gas cost 24457
// Error with parameter: gas cost 24660
function transferOwner1(uint256 tokenId, address newOwner) public {
if (_owners[tokenId] != msg.sender) {
revert TransferNotOwner();
// revert TransferNotOwner(msg.sender);
}
_owners[tokenId] = newOwner;
}
// require方法: gas cost 24755
function transferOwner2(uint256 tokenId, address newOwner) public {
require(_owners[tokenId] == msg.sender, "Transfer Not Owner");
_owners[tokenId] = newOwner;
}
// assert方法: gas cost 24473
function transferOwner3(uint256 tokenId, address newOwner) public {
assert(_owners[tokenId] == msg.sender);
_owners[tokenId] = newOwner;
}
}
